马耳他大学与其海上储能子公司FLASC合作,评估将可再生能源和储能解决方案与浮动防波堤相结合的潜力。

2018年在马耳他测试的FLASC浮式存储原型(由FLASC BV提供)
该项目名为FORTRES,由马耳他能源和水利局资助,将通过创建遮蔽水域来缓解恶劣天气下的挑战,同时提供长期储能服务,使防波堤能够发挥支持漂浮太阳能等可再生能源的双重作用。
随着海上活动的增加,浮式防波堤正成为深水区的首选方案,因为底部固定的传统布置通常仅限于浅水区。
浮动系统也可以安装在海底条件较差的地点,因为它们的安装和操作高度独立于海底特性。
此外,浮式防波堤结构能够在不影响底栖动植物群、阻挡水流、沉积物移动和鱼类迁徙的情况下衰减波浪。
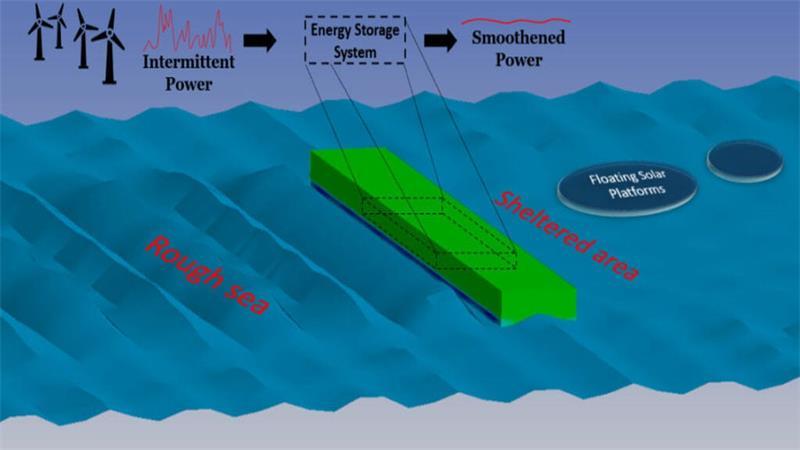
FORTRES项目目前正在模拟FLASC储能系统的运行,该储能系统集成在浮动防波堤中,以平滑来自同一位置的海上风力涡轮机和浮动太阳能平台的可再生能源间歇性供应。
尽管已经在海岸附近和码头部署了许多技术,用于防止海岸线侵蚀和缓解海上停泊活动,但部署在远离陆地的大规模浮动防波堤尚未在商业规模上得到证实。
FORTRES概念将能量储存集成在浮式防波堤内。使用ANSYS进行流体动力学模拟(由马耳他大学提供)
博士研究人员Charise Cutagar解释说,FORTRES项目旨在解决目前深海漂浮防波堤行为特征方面的知识差距,同时旨在通过整合储能来提高其可行性。
除了防波堤的几何形状外,系泊系统也被确定为决定浮式结构的波浪衰减能力的关键因素。
“利用真实的间歇功率数据对存储系统进行统计分析和数值建模,使我们能够预测并更好地了解当将存储系统合并到浮式防波堤的设计中时,如何有效地确定存储系统的尺寸。
博士研究员Andrew Borg表示:“了解存储系统容量和能源可用性之间的权衡为我们的下一步——分析整个项目的经济可行性——提供了良好的基础。”。
随着欧盟制定雄心勃勃的目标,通过绿色协议使其能源供应系统脱碳,探索可再生能源发电系统与海上储存系统合用的机会至关重要。
预计这种方法将能够更有效地利用海洋空间,同时避免在陆地上需要额外的空间来容纳储能基础设施。这对地中海中部的马耳他岛等岛屿来说可能非常有利,因为这些岛屿的陆地空间有限,无法容纳公用事业规模的可持续能源技术解决方案。
The University of Malta has teamed up with its offshore energy storage spin-off FLASC to assess the potential of integrating renewable energy and energy storage solutions with floating breakwaters.
The project, dubbed FORTRESS , which is being funded by the Malta Energy and Water Agency, will enable breakwaters to serve the dual role of supporting renewables such as floating solar by creating sheltered water areas to mitigate challenges in rough weather, while providing long duration energy storage services .
With increased offshore activity, floating breakwaters are becoming the preferred alternative in deep waters since bottom-fixed, conventional arrangements are typically limited to shallow waters.
The floating systems may also be installed at sites having poor seabed conditions as their installation and operation are highly independent of the seafloor characteristics.
Furthermore, floating breakwater structures have the ability to attenuate waves without affecting benthic flora and fauna, blocking water flow, currents, sediment movement and fish migration.
The FORTRESS project is currently simulating the operation of the FLASC energy storage system integrated into a floating breakwater when smoothing the intermittent supply of renewable energy from co-located offshore wind turbines and floating solar platforms .
Despite numerous technologies already deployed close to shores and in marinas which are used to protect against shoreline erosion and ease sea berthing activities, floating breakwaters of large scale deployed farther away from the landmass have not yet been proven on a commercial scale.
Doctoral researcher Charise Cutajar explained that the project FORTRESS seeks to address the present knowledge gap with regards to floating breakwaters behavioral characteristics in deep seas, while aiming to improve their viability through the integration of energy storage.
Alongside the geometry of the breakwater, the mooring system has also been identified as a critical factor that determines the wave attenuating capability of the floating structure.
“Statistical analyses and numerical modelling of the storage system with real intermittent power data have allowed us to predict and gain a better understanding of how to efficiently size the storage system when amalgamated within a floating breakwater’s design.
“Understanding the trade-off between storage system capacity and energy availability has provided a good foundation for our next step – that of analyzing the economic feasibility of the project as a whole,” stated doctoral researcher Andrew Borg .
As the EU sets ambitious targets to decarbonize its energy supply system through the Green Deal, it is essential to explore opportunities to co-locate renewable energy generation systems with storage at sea.
The approach is expected to enable more efficient use of marine spaces, while avoiding the need for additional space on land to accommodate energy storage infrastructure. This could be very beneficial for islands, such as the central Mediterranean island of Malta, which have limited space on land to accommodate utility-scale sustainable energy technology solutions.